Introduction
When choosing the best crusher for your primary, you first have to consider the application details. Desired product size, capacity, HGI, percentage of rock, and hardness of the rock in the feed are some of the factors that dictate the selection of primary crushing equipment.
Since many of the available types of crushers cross over application lines, other considerations, including space restrictions, mining methods and cost, may also figure into the final decision of crusher selection.
Let’s look at several different crushers used for the primary size reduction of coal.
Feeder-Breakers
Feeder-Breakers are designed for stationary, portable or semi-mobile crushing operations. They have enabled mine operators to increase production and improve material handling.

In general, Feeder-Breakers accept ROM feed material from the mine face and reduce it to a conveyable product for further size reduction. They can:
- Be located under hoppers to accept feed from haul trucks
- Have an integrated hopper to accept feed from loaders
- Be a dozer trap design with an open intake for charging by a dozer, shuttle car or other method
By design, Feeder-Breakers employ a drag chain/flight bar style conveyor connected at either end by steel shaft assemblies equipped with sprockets and bearings. The breaker mechanism is a horizontal rotor that crushes material against the flights and conveyor deck located toward the discharge end of the unit.
Depending on capacities, Feeder-Breakers may be a single or dual drag design. They are ideal for performing the primary crushing of ROM feed and reducing it to a conveyable product.
These units can handle feed sizes up to 72" and produce a nominal product size of between 6" and 14". Since Feeder-Breakers size in one dimension, secondary and tertiary crushing may be necessary to achieve the required final product size.

Rotary Breakers
Rotary Breakers are most often used in the processing of coal. They are especially useful when the feed streams have significant quantities of refuse in the form of rock, mine timbers, roof bolts, etc. that must be removed prior to further processing.
Rotary Breakers achieve reduction through attrition by repeatedly raising and dropping the feed material against strong, reinforced, perforated screen plates around the interior of the cylinder. The presence of hard rock in the feed assists in breaking the coal during the tumbling action.
Lifter shelves bolted to the cylinder interior raise the feed material and are adjustable for advancing or retarding the flow of material through the Rotary Breaker. This lifting and dropping action effectively breaks down the coal while passing the rock, tramp iron and mine timbers.
The desired product passes through the screen plate openings to a product belt below, while the rejected material is discharged out of the end of the cylinder with the aid of discharge plows.
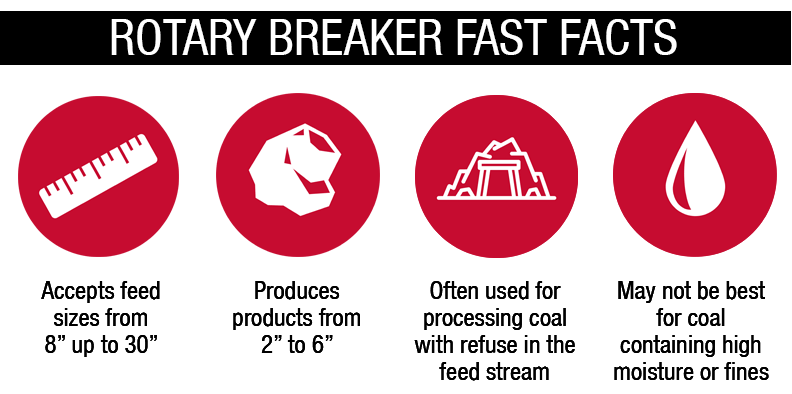
Rotary Breakers typically accept feed sizes from 8" up to 30" and produce products in the 2" to 6" range. The diameter and length of a Rotary Breaker is determined by various factors, including maximum feed size, HGI of the feed material, percent half size of the feed material, product size and percentage of refuse. Selection can be confirmed via drop/shatter testing.
Characteristics of the feed material are extremely important when considering Rotary Breakers.
Coals that are too hard or too woody (i.e. lignite) will not break up adequately, and a significant portion of the product may be discharged with the refuse.
If there is a low percentage of rock in the feed or if the rock is too soft, the coal may not break as desired. This can result in the product being rejected or the soft rock will breaking up and sending reject material to the product stream.
Coal containing a high moisture content with a high percentage of fines and/or clays can cause plugging of the screen plates, especially when smaller screen plate perforations are utilized.
Sizers
A Sizer is a direct-drive, low-profile crusher that is used for primary, secondary and tertiary reduction.
Sizers can accept material discharged directly from a loader or more uniformly from a conveyor belt, Vibratory Screen or Feeder. They are ideal for portable and in-pit crushing applications due to their low headroom.
Feed size, product size and capacity are the factors that normally determine the roll diameter and width of the Sizer. At times, the top size of the material may dictate the need for a much larger unit than suggested solely by the capacity requirements.
Primary Sizers are similar to traditional Double Roll Crushers in that they have two rolls with intermeshing teeth and crush inward, achieving a cubical product.
But the similarities end there. Sizers employ shaft-mounted gear reducer drive assemblies that provide low roll speeds, while relying on high torque to provide crushing power.
A torque limiting coupling is used between the reducer and motor to provide relief in the event of a stall due to an encounter with tramp steel or other uncrushable material.

Roll speeds of primary Sizers can be as much as four times slower than conventional belt-driven Roll Crushers. Because sizers use high-torque and low roll-speeds, they tend to fracture the material along natural cleavage lines, resulting in minimal fines generation.
Sizers are fed over the entire interior of the frame, allowing fines to pass through openings between crushing teeth and sizing combs. Theoretically, only the near-size and oversized material is crushed. Therefore, even with low roll speeds, relatively high throughput capacities can be achieved.
Typical roll diameters range from 20” to 60” (less the tooth height) and widths range from 48”– 144”. For primary sizers feed sizes range from 32”– 60” producing product sizes from 8”– 15”. A 4:1 ratio of reduction of feed to product size is considered when making crusher selection.
As with other crushers, the feed size normally determines the roll diameter and width of the sizer. However, an exception to this rule is sometimes encountered based on the coal properties or feed specifics.

Single Roll Crushers
With its 6:1 reduction ratio, the Single Roll Crusher is ideal for reducing large feed lumps to a medium size product, while also producing a considerably low percentage of fines. Minimum product sizing from a Single Roll Crusher is generally limited to 2” – 3”.
The crushing is carried out along the full width of the curved crushing plate and the low speed crushing roll. The curvature of the crushing plate provides an ample throat opening to capture large, irregular feed lumps. Replaceable crushing plate tips, or liners, are slotted to intermesh with the roll teeth to produce a cubical product that effectively reduces slabbing.

Single Roll Crushers are V-belt driven and employ a large diameter flywheel with a gear and pinion set to reduce roll speed. With the assistance of the inertia generated by the flywheel, this crusher is operated with relatively low horsepower and requires lower headroom compared to other crushers used for primary reduction.
Generally, belt-driven crushers employ some form of tramp relief mechanism to allow momentary movement of the crushing plate or one of the crushing rolls. This is accomplished with a mechanical spring and toggle mechanism.
Single Roll Crushers, while ideal for a variety of applications, are limited in throughput capacity and are, therefore, not applicable for many high tonnage requirements.

Double Roll Crushers
Belt-driven Double Roll Crushers can be used in primary crushing applications if sized properly, but they are typically used for secondary and tertiary reduction of various minerals.
The advantages to using Double Roll Crushers are numerous, including high capacity; low headroom; low horsepower; the ability to handle wet, sticky feeds; and generation of minimum fines while producing a cubical product.
As with other crushers, roll diameters and widths are dictated by the feed size, product size and capacity for the Double Roll Crusher. The rule of thumb for Double Roll Crusher ratio of reduction is 4:1.

The simplified design gives these units excellent reliability and requires very little maintenance. The crushers are designed with built-in tramp relief that allows for the passing of uncrushable materials for continuous operation. Once the uncrushable has been passed, the crusher returns to the initial product setting.
In a Double Roll Crusher, all feed material must pass between the crushing rolls, which promote inter-particle crushing as well as mechanical crushing.
With a variety of roll surface designs, this crusher is capable of producing a much finer product than any of the other crushers referenced.

Two-Stage Roll Crushers
Two-stage Roll Crushers, such as the Triple and Quad Roll Crushers, are also belt-driven. They are capable of performing primary and secondary or secondary and tertiary crushing in a single pass through one machine.
Both Triple and Quad Roll Crushers reduce ROM feed material to marketable sizes.

Depending on the design, the primary stage of the crusher is comprised of either a single roll or double roll layout. The primary stage receives the feed material and accomplishes the initial reduction prior to the secondary bottom stage.
The secondary bottom stage of either model is made up of a double roll configuration, which receives the material from the top stage and performs the final size reduction.
The two-stage design combined with the proper tooth configuration produces a uniform, cubical product with minimum fines. Higher roll speeds, which are made possible by utilizing belt drives, allow for tremendous throughput capacity.
Generally, a Quad Roll Crusher is recommended for a medium size feed material, while the Triple Roll Crusher, with its single roll top stage, is effective for handling larger size feeds.
These machines do the work normally assigned to two separate crushers. Typical feed sizes range from 18” – 72” with final product size of ½” – 3”.

Selecting the right primary crusher
Many factors play a part in the selection of the proper primary crushing equipment, and in many applications, there is more than one correct choice.
Contact a crusher manufacturer to review your applications details. They can outline all the available options and provide a professional recommendation for your coal project.














